Newborn screenings
The aim of newborn screening is to detect certain hereditary or congenital conditions as early as possible, which, if untreated, could compromise the child’s health or development.
All newborns born in Estonia are offered screening for 21 different congenital diseases. This is free of charge for children with health insurance.
Newborn hearing tests
The very first test done after birth, known as the newborn hearing screening, is the otoacoustic emissions test (OAE). It is a quick test to assess whether the cells in the child’s hearing organs are in good order. During the test, quiet sounds are played into the child's ear and if the cells are functioning properly, the instrument can detect the response from the cells (known as sound reflection).
This test is very quick and safe, but it may need to be repeated. Usually, one ear is tested at a time, but this procedure may vary slightly depending on the tester. The child may be asleep during the test, which often makes testing even easier and faster.
The device indicates whether the ear passes the test or not, but it does not assess the child’s level of hearing. Minor hearing deficits may also go undetected with this test.
There are a number of reasons why a child may not pass the test the first time and in such cases the test is repeated. If the child fails the screening test repeatedly, they will be referred for further examinations.
Newborn hearing tests are safe.
Assessment of the red reflex of the eyes
A red reflex test, known as the Brückner test, is done on all newborns who are discharged.
Checking the red reflex using an ophthalmoscope – light is directed into both eyes at the same time to assess the red reflex of both eyes simultaneously. In the case of a normal pupil (Photo 1), the pupillary reflexes should be equally reflected from both eyes. Red reflexes may be disrupted in a range of eye disorders.
Red reflex normal finding. The normal finding is that the reflexes are equally reflected from both eyes.
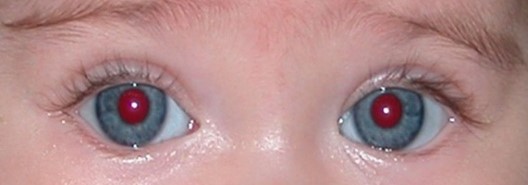
Photo 1. Red reflex, e.g. Brückner test normal finding.
 Terviseportaal
Terviseportaal