Examination of uterine cavity with saline solution
The purpose of this leaflet is to provide the patient with information about the examination of the uterus with saline solution.
Indications
Examination of the uterus with saline solution is a method for detecting diseases of the lining of the uterus – endometrium – such as uterine polyps, myoma nodes, etc. The saline solution introduced into the uterine cavity pushes the walls of the uterine cavity slightly apart, after which the formations in the uterine cavity are more visible with an ultrasound.
The best time to do the examination is from the 7th to the 12th day of the menstrual cycle. During this period of the cycle, the endometrium is the thinnest, making it the best moment to evaluate it for any pathologies.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the examination include:
- pregnancy;
- inflammatory process in the lesser pelvic organs;
- intrauterine contraceptive device.
Before the examination
The examination may be uncomfortable but is not usually painful. If you wish, an over-the-counter painkiller may be taken one hour before the examination.
Course of the examination
The examination takes around half an hour. The bladder should be emptied prior to the examination to ensure better visibility on the ultrasound. The examination is performed in a gynaecological chair: it starts with a vaginal ultrasound examination during which the structure of the uterus, endometrium and ovaries are assessed. The ultrasound sensor is covered with a special protective coating on which the gel is applied, after which the sensor is inserted into the vagina. The ultrasound itself takes a few minutes, after which the sensor is removed from the vagina. Next, a gynaecological mirror is placed into the vagina, the vagina and cervix are cleaned and, if necessary, anesthetised with a local analgesic gel.
The cervix is fixed and a thin catheter is inserted into the uterine cavity. When the catheter is in place, the gynaecological mirror is removed. A gel-coated ultrasound sensor is re-inserted into the vagina, sterile saline is introduced into the uterine cavity through the catheter (Figure 1) and ultrasound is performed simultaneously.
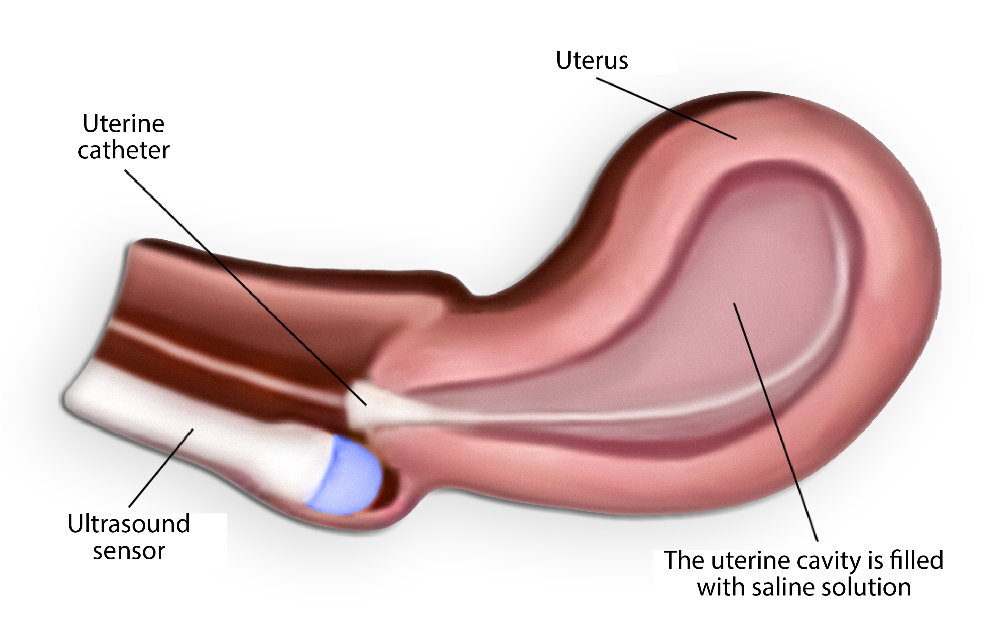
Figure 1. Filling the uterine cavity with saline through the catheter
During the introduction of saline into the uterine cavity, a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen may occur, with a slight pain resembling menstrual pain.
After the examination, the saline introduced into the uterine cavity is excreted through the cervix. There may be a small amount of staining flow during the few days after the procedure; no special regimen is required.
The doctor who performed the examination will explain the findings of the examination; further treatment will be explained by your treating doctor.
ITK1081
Approved by the decision of the Care Quality Commission of East Tallinn Central Hospital on 20.04.2022 (protocol no. 6-22)
 Terviseportaal
Terviseportaal